Macro Nutrients for Cannabis
“Macro-nutrients” is a term that regroups 3 nutrients necessary for a healthy plant. All of these are mobile, which means that the plant can reallocate them from one part to another.
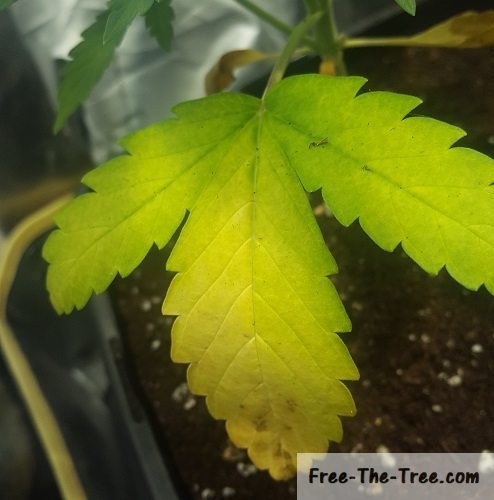
For example, it needs some Nitrogen to grow new foliage. The plant can take the Nitrogen from lower leaves and reallocate it to this new growth. While doing so you will notice the older leaves turning yellow. The typical sign of Nitrogen deficiency
Related Articles

Guides
Mobile and Immobile Marijuana Nutrients
The 3 macro nutrients are:
Nitrogen (N)
Marijuana looooves Nitrogen and requires high levels of it during the vegetative stage. Once you get into the flowering stage its need drops drastically. You’ll understand quickly why in the “purpose” section.
Nitrogen is a nutrient that easily washes away from the soil. It needs to be replaced regularly, especially during vegetative growth.
If there’s an excess of Nitrogen when harvesting the plant the buds won’t have as good of a taste and won’t burn well. This is one of the reasons why it’s important to flush well your plants before the harvest.
The Purpose of Nitrogen
Nitrogen regulates the cannabis’s ability to make proteins. These proteins are essential for new protoplasm in the cells.
Nitrogen allows the plant to tie proteins, hormones, chlorophyll, vitamins and enzymes together.
It is also essential for the production amino acids, enzymes, nucleic acids, chlorophyll and alkaloids.
This important nutrient is mainly responsible for leaf and stem growth as well as overall size and vigor.
Nitrogen is most active in young buds, shoots and leaves. Ammonium (NH4+) is the most readily available form of nitrogen.
If you use this, be careful not to use too much since it can easily burn the plants.
The Nitrate form of nitrogen is much slower to assimilate than ammonium. As such, it will release much slower in the soil. Hydroponic fertilizers use this slower-acting nitrogen compound and mix it with ammonium.
Related Articles

Guides
Nitrogen Deficiency ? How to Spot and Deal with It
Phosphorus (P)
Cannabis uses the phosphorus during all stages of it life and has a different purposes at each stage.
During the vegetative stage, it’s mainly used for root development. On the other hand during the flowering stage one of its uses is bud growth.
Phosphorus is one of those extremely important nutrients.
Just like Nitrogen, Phosphorus is a Mobile element. This means that the plant can reallocate it where ever it’s needed
Purpose of Phosphorus
Phosphorus is necessary for photosynthesis. It also provides a mechanism for the plant to transfer energy within itself.
It’s also one of the components of DNA and is associated with overall vigor, resin and seed production.
The highest concentrations of Phosphorus are found in the root-growing tips, growing shoots and vascular tissue.
Related Articles

Guides
Phosphorus Deficiency | Identifying and Solving the issue
Potassium (K)
Potassium is used at all stages of growth. Soils with a high level of potassium increase a plant’s resistance to bacteria and mold.
Purpose of Potassium
Potassium helps combine sugars, starches and carbohydrates. These combinations are essential for growth by cell division.
It also increases the chlorophyll in the foliage and helps to regulate the stomata openings. This allows plants to make better use of the light and air.
Potassium is essential in the accumulation and translocation of carbohydrates. Furthermore, it’s necessary to make the proteins that increase the oil content and improve the flavor in cannabis plants.
And finally, Potassium encourages strong root growth, it is associated with disease resistance and.. water intake.
So yeah, also a pretty important nutrient 🙂
Related Articles

Guides