Soil for Cannabis
You may have heard this thousands of times, but one of the most important things is the soil you choose and how you treat it.
Three basic factors contribute to a good soil for Cannabis
3 factors for a good soil to grow cannabis:
- Texture: The soil shouldn’t be too compact and this for 3 reasons. Roots need to be able to grow easily. They need an oxygen flow, which isn’t the case when its too compact, and last but not least drainage! If your soil is compact water won’t be able to flow.
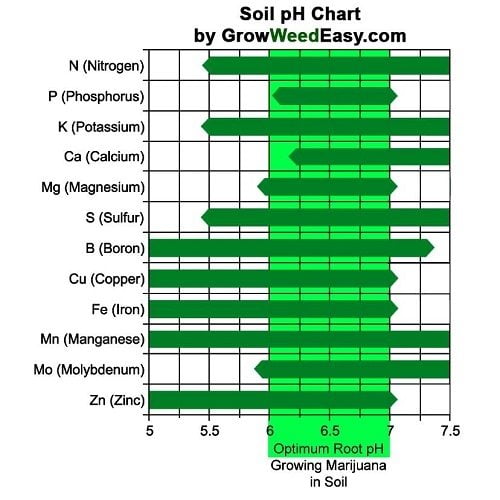
- pH: pH level of the soil is critical since the absorption of nutrients by the roots depends on the pH.
Aim for a pH between 6.5 and 6.8 you should be good. - Nutrient Content: Last but not least, nutrients.. Obviously, your soil must have nutrients, whether this is achieved by compost, companion plants and micro-organisms, or bought already enriched.
Now that we’ve gone over this, let’s go in depth the different soils and amendments to grow cannabis
Types of soils and their Textures
There are globally 3 types of soils, clay or adobe soil, sandy soils and loom soil that we’ll cover.
Clay soils (aka adobe soils)
Adobe soil is made up of very small, flat mineral particles. When these particles get wet, they pack tightly together which will slow or stop root penetration and water drainage.
With this type of soil marijuana roots won’t be able to breath because of the very little (or no) space left for oxygen to passe through.
When watering the irrigation of these types of soil is very slow and once irrigated drainage is very slow which and drown the roots.
For these reasons, clay soils clay to grow cannabis
Sandy soils
Sandy soils are composed of large particles that allow a good supply of oxygen and drainage.
The main downside the sandy soils would be that there’s too much drainage, the water retention is so low that you’ll have to water very frequently.
Marijuana roots should develop without a problem in sandy soil since it has good air and water holding capabilities.
How to check soil texture quality for cannabis?
In order to see if the texture of the soil is good to grow you weeds pick up a handful of moist (not wet or soggy) soil and gently squeeze it.
The soil should barely stay together and have a little of a sponge-like effect when you slowly open up your hand.
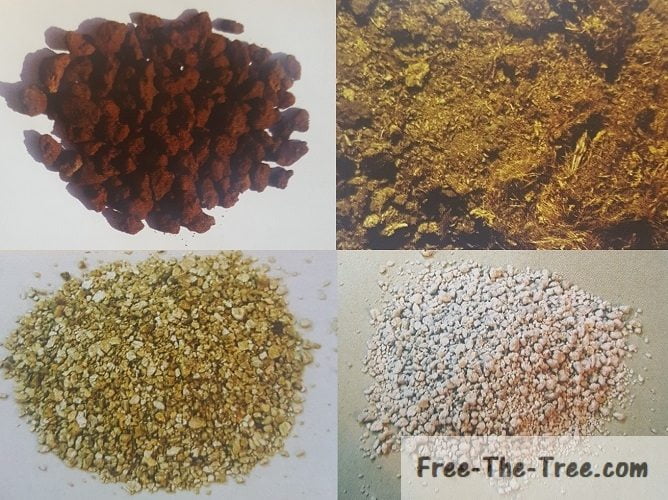
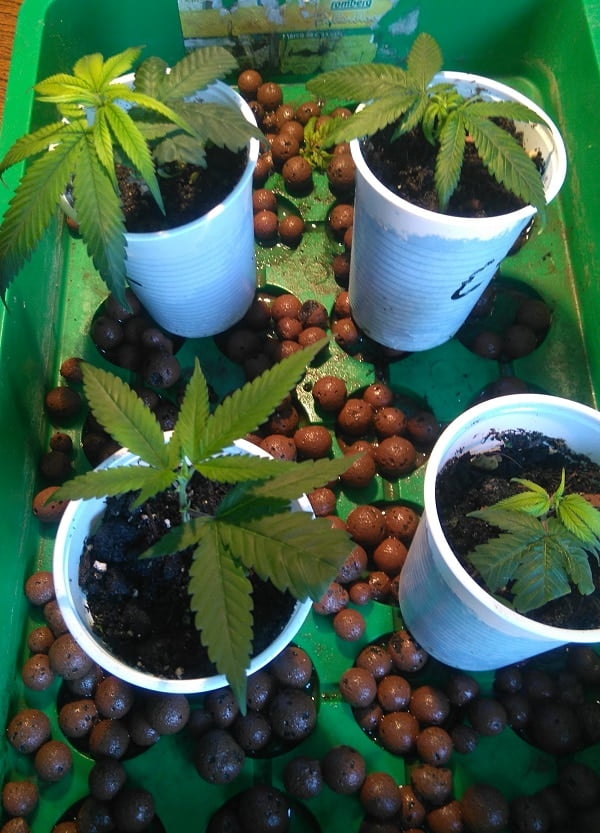
For indoor soil make sure you have a rotation and you have soil amendments. The best thing is to have micro-organic life and companion planting, even in your indoor soil, remember all we’re doing is replicating nature.